Structure Optimization of Gatastatin for the Development of γ-Tubulin-Specific Inhibitor
Kana Shintani, Haruna Ebisu, Minagi Mukaiyama, Taisei Hatanaka, Takumi Chinen, Daisuke Takao, Yoko Nagumo, Akira Sakakura, Ichiro Hayakawa,* Takeo Usui*
ACS Med. Chem. Lett.2020, 11 (6), 1125–1129. (Published online: March 30, 2020)
DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00526 
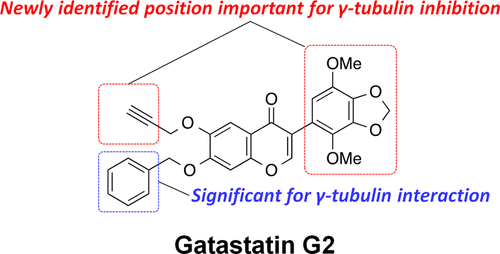
Gatastatin (O7-benzyl glaziovianin A) is a γ-tubulin-specific inhibitor that is used to investigate γ-tubulin function in cells. We have previously reported that the unsubstituted phenyl ring of the O7-benzyl group in gatastatin is important for γ-tubulin inhibition. To obtain further structural information regarding γ-tubulin inhibition, we synthesized several gatastatin derivatives containing a fixed O7-benzyl moiety. Modifications of the B-ring resulted in drastic decrease in cytotoxicity, abnormal spindle formation activity, and inhibition of microtubule (MT) nucleation. In contrast, various O6-alkylated gatastatin derivatives showed potent cytotoxicity, induced abnormal spindle formation, and inhibited MT nucleation. We had previously reported that O6-benzyl glaziovianin A is a potent α/β-tubulin inhibitor; thus, these new results suggest that the O6-position restricts affinity for α/β- and γ-tubulin. Considering that an O7-benzyl group increases specificity for γ-tubulin, more potent and specific γ-tubulin inhibitors can be generated through O6-modifications of gatastatin.