
Microfluidics
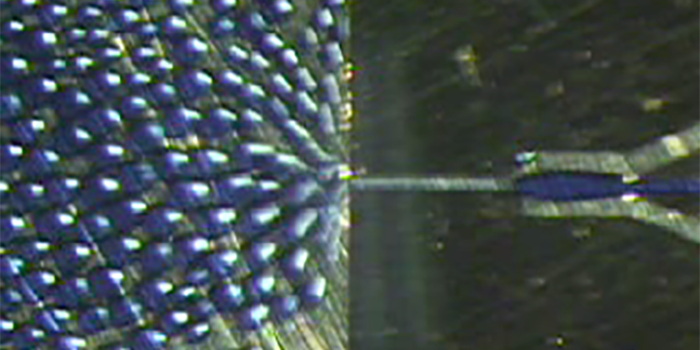
Microfluidic channel is a general term for a channel that has a thin channel about the size of a hair. The fluid flowing in a microchannel is laminar due to its low Reynolds number. Therefore, the microfluidic channel is a favorable environment for the formation of uniformly sized droplets and stable jet flow. We develop processes to prepare microparticles and nanofibers using uniformly sized droplets and jet flows formed in microchannels as templates. In addition to experimental studies, we perform numerical simulations of fluid flow in microchannels using COMSOL Multiphysics®, a general-purpose computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation software. Specifically, CFD simulations are used to design microfluidic devices suitable for droplet generation and jet flow formation.
In microfluidic channels, the direction of fluid flow can be regarded as the time evolution of the phenomenon. We thus study the formation of microparticles and fibers from droplets and jets by directly observing the flow in the microfluidic channel with a high-speed camera.
Microfluidic Emulsification
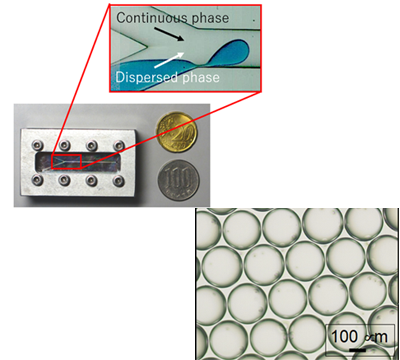 Microfluidic device is a small device that has a channel in the order of several tens to hundreds micrometer in width, enabling the generation of precision pico-liter scale emulsion droplets. Uniform Water-in-Oil (W/O) emulsion droplets and Oil-in-Water (O/W) emulsion droplets are continuously generated at the junction where the dispersed phase and the continuous phase meet, under low Reynolds number flow condition. In addition, by altering flow conditions such as fluid viscosity, interfacial tension, flow rate ratios, we can control the resultant droplet sizes. Furthermore, mass-production of emulsions can be achieved by increasing the number of devices (numbering up).
Microfluidic device is a small device that has a channel in the order of several tens to hundreds micrometer in width, enabling the generation of precision pico-liter scale emulsion droplets. Uniform Water-in-Oil (W/O) emulsion droplets and Oil-in-Water (O/W) emulsion droplets are continuously generated at the junction where the dispersed phase and the continuous phase meet, under low Reynolds number flow condition. In addition, by altering flow conditions such as fluid viscosity, interfacial tension, flow rate ratios, we can control the resultant droplet sizes. Furthermore, mass-production of emulsions can be achieved by increasing the number of devices (numbering up).
The target of our study includes the design of microchannel, material preparation process, and development of mass-production process using microfluidics.
- References
J. Kubota et al., Colloid Surf. A 302, 320–325 (2007)
E. Kamio et al., Lab Chip 9, 1809–1812 (2009)
T. Harada et al., Jap. J. Appl. Phys., 49, 07HE13 (2010)
Modeling of Jetting Formation
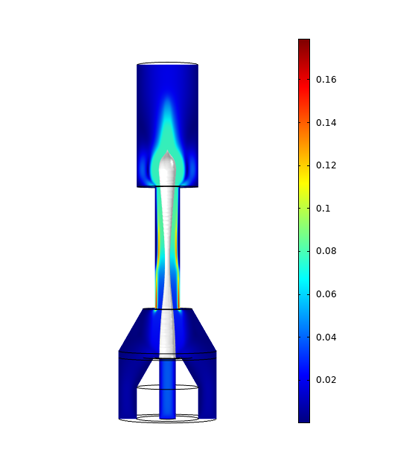 We study the preparation of micro-/nano-fibers using a microchannel wet spinning process. In this method, we use a microfluidic device made of stainless steel, so we cannot observe the inside of the device during fiber preparation. Therefore, we analyze the fluid behavior inside the device by CFD simulations using COMSOL Multiphysics® to search for fluid feeding conditions and to improve the device structure for stable spinning.
We study the preparation of micro-/nano-fibers using a microchannel wet spinning process. In this method, we use a microfluidic device made of stainless steel, so we cannot observe the inside of the device during fiber preparation. Therefore, we analyze the fluid behavior inside the device by CFD simulations using COMSOL Multiphysics® to search for fluid feeding conditions and to improve the device structure for stable spinning.
CFD Simulation of Droplet Formation in a Microchannel
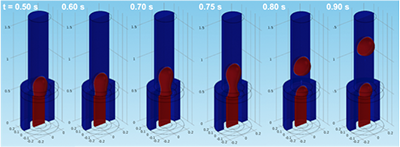 We prepare microparticles and microcapsules using a droplet-based microfluidic process. When designing a new microfluidic channel, we use CFD simulation to determine the device geometry suitable for droplet generation.
We prepare microparticles and microcapsules using a droplet-based microfluidic process. When designing a new microfluidic channel, we use CFD simulation to determine the device geometry suitable for droplet generation.
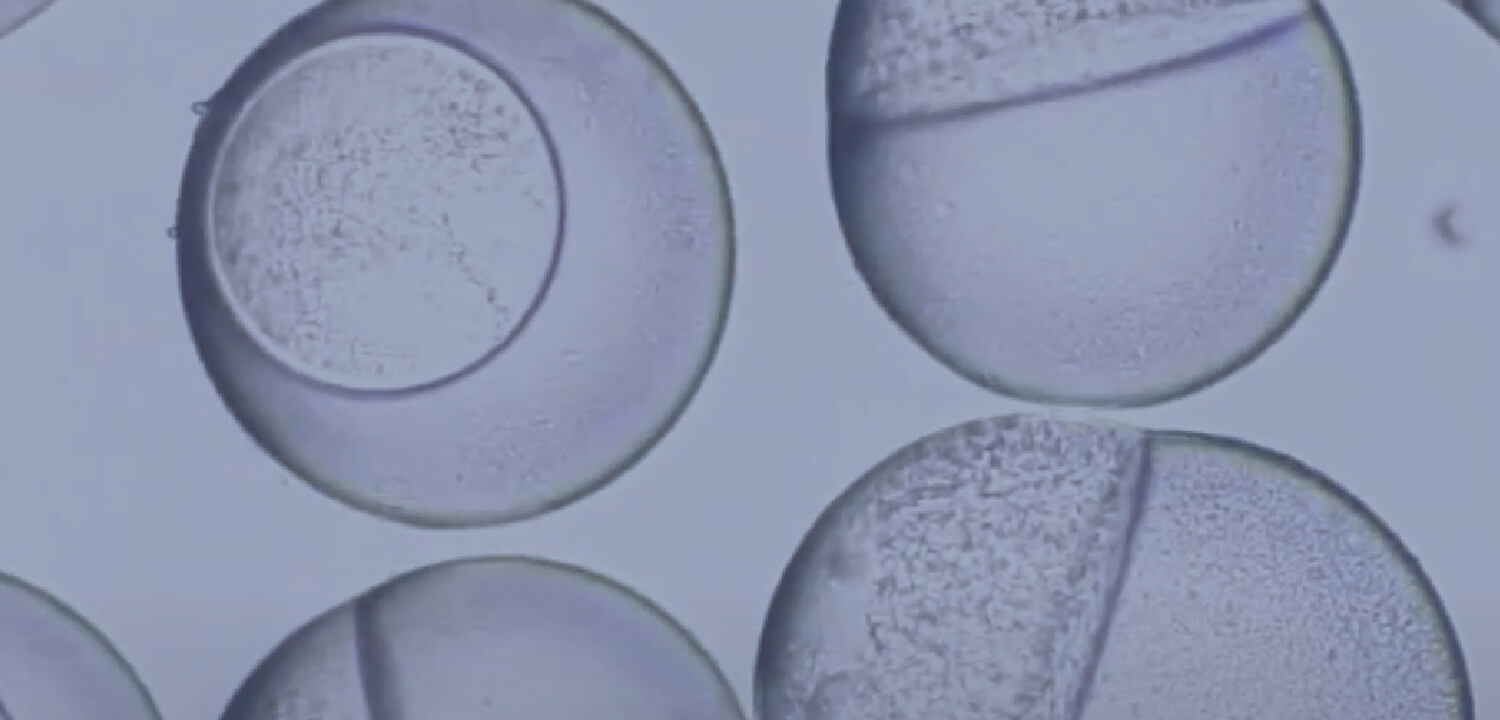
in situ Observation of Phase Separation in a Single Droplet
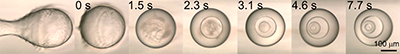 In a microfluidic channel, the direction of fluid flow can be regarded as the time evolution of the phenomenon. By directly observing monodisperse droplets flowing in a microfluidic channel with a high-speed camera, we have achieved temporal observation of phase separation phenomena occurring within a few seconds in droplets. Using this technique, we study the mechanisms of phase separation phenomena that are difficult to analyze in batch systems.
In a microfluidic channel, the direction of fluid flow can be regarded as the time evolution of the phenomenon. By directly observing monodisperse droplets flowing in a microfluidic channel with a high-speed camera, we have achieved temporal observation of phase separation phenomena occurring within a few seconds in droplets. Using this technique, we study the mechanisms of phase separation phenomena that are difficult to analyze in batch systems.